Artificial Intelligence (AI) has steadily shifted from a distant dream to an integral part of daily life, influencing industries, reshaping economies, and redefining human potential. Once confined to science fiction,
AI is now leading cutting-edge innovations across various sectors, powering technologies that have altered how we live, work, and communicate. In this article, we explore the origins of AI, its advancements, and the profound impact it has on society.
Table of Contents
The Origins and Evolution of AI

The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined in 1956 by computer scientist John McCarthy at a workshop at Dartmouth College. Back then, AI was defined as the science and engineering of creating machines capable of performing tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning.
Early developments in Artificial Intelligence focused on symbolic methods, where machines were programmed with explicit rules to make decisions. These systems, known as expert systems, were the first attempts to create intelligent behavior in machines.
They performed reasonably well in narrow, specialized domains such as medical diagnosis and chess. However, they lacked the ability to learn or generalize knowledge to new problems.
AI faced several setbacks, often called “Artificial Intelligence winters,” where progress stagnated due to over-promises and under-delivery. Yet, with exponential advances in computing power, machine learning algorithms, and access to massive data sets, AI has now entered an era of rapid development.
Key AI Technologies Shaping the Future
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is one of the core subsets of AI. It allows systems to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. The rise of ML has been fueled by vast amounts of data generated by digital platforms, social media, and IoT devices.

One of the most significant developments in ML is the introduction of deep learning a type of ML that mimics the structure of the human brain using artificial neural networks. Deep learning models are used in many applications today, including image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing (NLP).
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is a branch of Artificial Intelligence that deals with the interaction between computers and humans using natural language. This technology has improved significantly in recent years, thanks to advancements in ML and deep learning.
From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to chatbots that handle customer service, NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. These systems are now used in various applications, including translation services, sentiment analysis, and automated writing tools.
3. Computer Vision
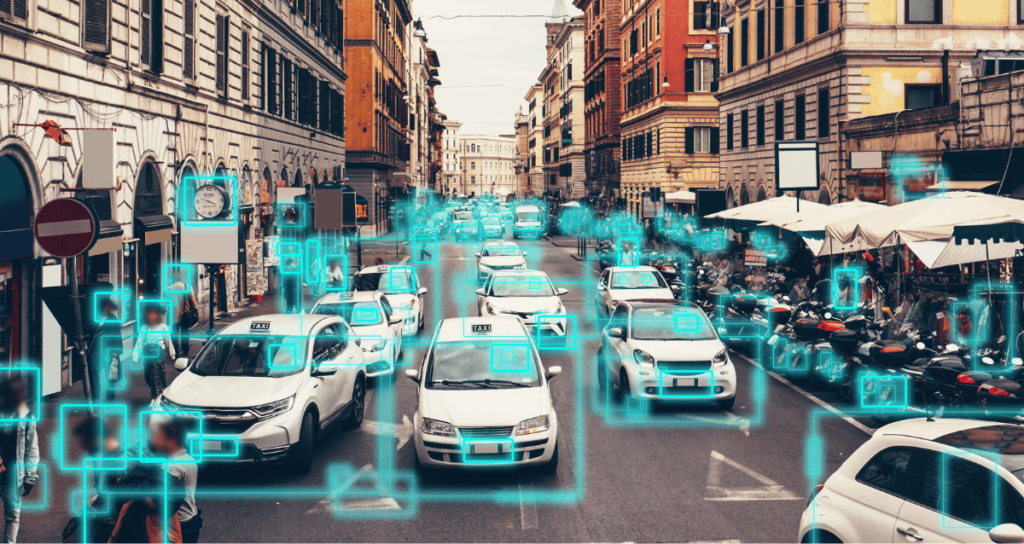
Computer vision is another prominent Artificial Intelligence technology that enables machines to understand and interpret visual information from the world, similar to human sight. AI-powered computer vision systems are used in self-driving cars, facial recognition, and even healthcare for medical image analysis.

The integration of computer vision in industries such as retail, security, and automotive has revolutionized how machines interact with their environments, leading to innovations like autonomous drones, real-time video analysis, and augmented reality applications.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is an AI technology that allows businesses to automate routine, repetitive tasks through the use of software robots. These robots can mimic human actions such as data entry, processing transactions, and responding to simple queries.
By automating mundane tasks, RPA frees up human workers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their jobs, leading to enhanced productivity and efficiency across industries such as finance, insurance, and customer service.
5. Generative AI
Generative AI is a form of Artificial Intelligence that can create new content, such as images, text, or music, based on input data. Recent breakthroughs in generative AI, like OpenAI’s GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)** models, have demonstrated the potential of AI in creative fields.
Generative AI can be used to write articles, compose music, create art, and even develop software code. This has opened up new possibilities in industries like entertainment, marketing, and product design, where AI-generated content is becoming increasingly valuable.
The Impact of AI on Society
1. AI in Healthcare
AI has the potential to transform healthcare by improving diagnostics, enhancing patient care, and enabling more personalized treatments. AI algorithms can analyze medical data, including imaging, pathology slides, and patient histories, to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases such as cancer or predicting patient outcomes.

Additionally, AI-powered wearable devices and mobile apps are helping people monitor their health in real-time. For instance, AI-based heart rate monitoring tools or glucose level trackers provide users with actionable insights and help doctors remotely monitor their patients.
One of the most promising areas is precision medicine, where AI analyzes a patient’s genetic data to recommend tailored treatments, improving the effectiveness of interventions.
2. AI in Business
AI is revolutionizing how businesses operate by streamlining processes, enhancing decision-making, and improving customer experiences. AI-powered analytics tools help organizations make data-driven decisions, identify market trends, and optimize marketing strategies.
In e-commerce, Artificial Intelligence helps personalize shopping experiences, recommend products, and manage inventory more efficiently. Chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer inquiries around the clock, providing quick, automated responses while reducing the workload on human support teams.
Supply chain management is also becoming more efficient, with AI predicting demand, optimizing routes, and reducing delivery times.
3. AI in Education
Education is another sector undergoing a transformation due to AI. Intelligent tutoring systems, personalized learning platforms, and AI-driven assessment tools are reshaping traditional learning environments.

Artificial Intelligence helps educators identify students’ strengths and weaknesses, tailoring lessons to individual needs. This allows for personalized learning experiences, where students can progress at their own pace, making education more inclusive and effective.
AI-powered tools also assist in grading assignments, saving teachers time and ensuring consistent evaluation standards.
4. AI in Transportation
Self-driving cars are the most notable example of AI’s potential to revolutionize the transportation industry. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber are developing autonomous vehicles that rely on AI algorithms to navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make real-time decisions.
AI is also being used in traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve public transportation services. In logistics, AI-powered drones and robots are being deployed to streamline delivery processes and improve supply chain efficiency.
5. AI and Ethical Concerns
While the benefits of AI are numerous, its rapid growth raises several ethical concerns that society must address. Issues such as bias in Artificial Intelligence algorithms, job displacement due to automation, and the potential misuse of AI technologies (e.g., deepfakes or autonomous weapons) require thoughtful consideration.
AI systems learn from data, and if the data contains biases, the Artificial Intelligence will likely replicate and even amplify these biases. For instance, facial recognition systems have been shown to perform worse on individuals with darker skin tones, highlighting the need for transparency and fairness in AI development.
Additionally, automation poses a risk to jobs, particularly in industries such as manufacturing, retail, and customer service. As machines take over routine tasks, it’s essential for society to invest in retraining programs and reskilling workers to adapt to the changing job landscape.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
As AI continues to evolve, its capabilities will only expand. Emerging technologies such as **quantum computing** hold the potential to exponentially increase AI’s processing power, enabling more complex and sophisticated models.
Moreover, AI will likely play a crucial role in tackling global challenges such as climate change, disease outbreaks, and resource scarcity. AI-driven climate models can predict the impact of human activities on the environment, while Artificial Intelligence in agriculture can improve crop yields and reduce waste.
At the same time, as AI becomes more integrated into society, it is essential to prioritize human-centric AI development that ensures fairness, transparency, and accountability. Building trustworthy AI systems that respect privacy and promote ethical practices will be key to unlocking AI’s full potential.
Conclusion
AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a present reality transforming every aspect of society. From healthcare and business to education and transportation, AI is enhancing human capabilities, improving efficiency, and creating new opportunities.
However, with great power comes great responsibility. As we embrace AI’s advancements, it is crucial to address the ethical challenges it presents to ensure that the technology benefits all of humanity. By fostering innovation while upholding ethical standards, we can harness AI to create a better, more equitable future for everyone.
The future of Artificial Intelligence is full of promise, and we are only at the beginning of this technological revolution.
For find more informational content related to AI please also check the Blog Page.

Great insights Shashi. Keep working like this😁
Yeah sure Dude!